Retinoid
The retinoids are a class of chemical compounds that are natural derivatives of vitamin A or are chemically related to it. Synthetic retinoids are utilized in cosmetic formulations, clinical dermatology, and the treatment of some forms of cancer.[1]
Retinoids have many important functions throughout the body, including in vision,[2] regulation of skin proliferation and differentiation, growth of bone tissue, immune function,[3] and male fertility.[4]
The biology of retinoids is complex, having well-documented effectiveness in the management of conditions ranging from acute promyelocytic leukemia to acne to photoaging.[5] On the other hand, retinoids may be involved in metabolic dysfunction and, at least in some forms, carcinogenesis.[6][7]
Types
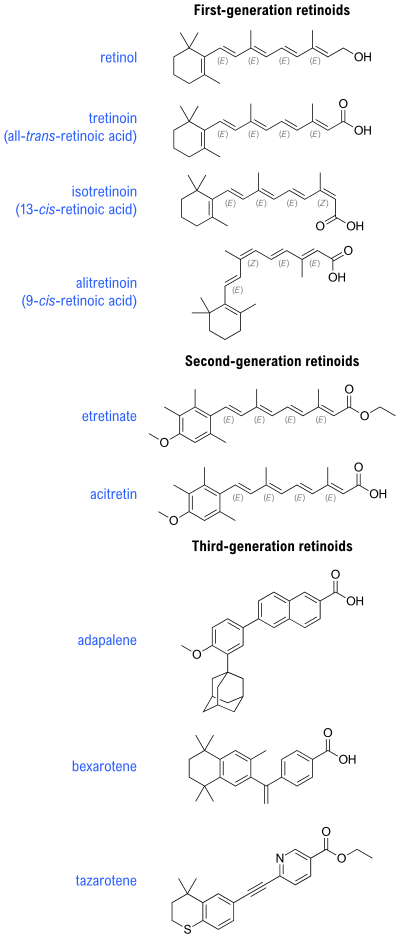
[edit]Retinoids are divided into four generations based on their molecular structure and receptor selectivity.[8]
| Generation | Description | Compounds |
|---|---|---|
| First generation | Isomers and naturally occurring compounds | retinol, retinal, tretinoin (retinoic acid), isotretinoin, and alitretinoin |
| Second generation | Synthetic analogs formulated for oral dosing. There are no topically available second generation formulations of retinoids. | etretinate and its metabolite acitretin |
| Third generation | Retinoidal benzoic acid derivatives | adapalene, bexarotene, and tazarotene |
| Fourth generation | Topical retinoid with selectivity towards the RAR receptor located in the epidermis. | Trifarotene, seletinoid G |
Structure
[edit]The basic structure of the hydrophobic retinoid molecule consists of a cyclic end group, a polyene side chain and a polar end group. The conjugated system formed by alternating C=C double bonds in the polyene side chain are responsible for the color of retinoids (typically yellow, orange, or red). Hence, many retinoids are chromophores. Alternation of side chains and end groups creates the various classes of retinoids.[citation needed]
First generation retinoids are produced naturally in the body and interact with their normal biological counterparts, such as retinol binding protein 4 for retinol, retinoid receptors for all-trans-retinoic acid or 9-cis-retinoic acid.[9] 13-cis retinoic acid has an unknown biological pathway but appears to act as a growth factor.[10]
Second generation retinoids have a mixed effect and interact mainly with signaling in the skin.[11][failed verification]
Third generation retinoids have narrow biological roles due to their constrained structure, with adapalene mimicking the effects of isotretinoin,[12] bexarotene binding only the Retinoid X receptors, and tazarotene binding the Retinoic acid receptor beta and Retinoic acid receptor gamma forms.[13]
The only fourth generation retinoid, Trifarotene, binds selectively to the RAR-y receptor. It was approved for use in the US in 2019.[14]
Pharmacokinetics
[edit]The major source of retinoids in human diet are plant pigments such as carotenes and retinyl esters derived from animal sources.[15] Retinyl esters are transported through the chylomicron pathway to the liver or fat tissue while retinol or carotenes are transported from the enterocytes to the liver and are processed into retinyl esters by LRAT for storage.[16] Most synthetic retinoids are absorbed when taken orally while topical retinoids cannot diffuse through the skin barrier unless it is compromised.[12]
All classes of retinoid bind to many proteins. Natural retinoids such as retinol and retinyl esters bind to carrier proteins such as RBP4, chylomicrons and VLDL while synthetic retinoids likely bind to these and other proteins.[17] First generation retinoids are rapidly metabolized by Cytochrome p450 enzymes, typically of the Cyp26 family.[18] Later generation retinoids are resistant to Cyp26 metabolism and remain in the body for much longer.[citation needed]
Uses
[edit]Common skin conditions treated by topical retinoids include acne, psoriasis,[19][20] and effects of photoaging.[21][22] In addition, retinoids are used to treat some rare skin disorders, including discoid lupus[23] and mycosis fungoides.[24] In Japan, isotretinoin may be used for neuroblastoma treatment,[25] but it is not approved in other countries due to a lack of consistency in studies of its effectiveness.[26] Oral retinoids are readily toxic, requiring consistent clinical oversight, and are approved in several diseases for which said toxicity is paradoxically useful, including acute promyelocytic leukemia, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, and heterotopic ossification.[27]
Toxicity
[edit]Toxic effects of retinoids occur with both acute or prolonged intake, depending on which retinoid is considered. The specific toxicity is related to the mechanism of action as well as exposure. A medical sign of chronic or acute poisoning with retinol is hypervitaminosis A, which includes the presence of painful tender swellings on the long bones. Anorexia, skin lesions, hair loss, hepatosplenomegaly, papilloedema, bleeding, general malaise, pseudotumor cerebri, and death may also occur.[28] Similar effects occur with other retinoids, except for 13-cis retinoic acid and its derivatives, such as adapalene.[citation needed]
Retinoids provoke rapid elevation of circulating triglycerides leading to hypertriglyceridemia as well as cholesterol, leading to hypercholesterolemia.[29] Retinoids are further shown to worsen many metabolic diseases, such as diabetes and congestive heart failure. Large-scale randomized, controlled clinical trials have conclusively shown that vitamin A, retinol and other retinoids increase mortality and cancer rates.[30][31] In addition to the harmful effects shared by other retinoids, bexarotene causes severe hypothyroidism.[32]
The Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC), based on its review, confirmed that taking oral retinoids during pregnancy can have harmful effects on the baby as they may cause CNS, cranio-facial, cardiovascular and other defects.[33][34] The use of acitretin, alitretinoin and isotretinoin should be prohibited in women of childbearing age unless they take measures to prevent pregnancy.[35] The use of topical retinoids should also be excluded during pregnancy and in women planning pregnancy.[citation needed]
Many lotions that claim to prevent or treat stretch marks contain retinol, which is not an ingredient that is safe for pregnant women.[36][37] The Association of the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) recommends that pregnant women consult a health care provider before trying any lotions or oils for stretch mark prevention.[38]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Motamedi M, Chehade A, Sanghera R, Grewal P (2022). "A Clinician's Guide to Topical Retinoids". Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery. 26 (1): 71–78. doi:10.1177/12034754211035091. ISSN 1203-4754. PMC 8750127. PMID 34292058. Retrieved 30 Dec 2024.
- ^ Kiser PD, Golczak M, Palczewski K (January 2014). "Chemistry of the retinoid (visual) cycle". Chemical Reviews. 114 (1): 194–232. doi:10.1021/cr400107q. PMC 3858459. PMID 23905688.

- ^ Hall JA, Grainger JR, Spencer SP, Belkaid Y (July 2011). "The role of retinoic acid in tolerance and immunity". Immunity. 35 (1): 13–22. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2011.07.002. PMC 3418663. PMID 21777796.
- ^ Topping T, Griswold MD (2022-04-28). "Global Deletion of ALDH1A1 and ALDH1A2 Genes Does Not Affect Viability but Blocks Spermatogenesis". Frontiers in Endocrinology. 13: 871225. doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.871225. PMC 9097449. PMID 35574006.
- ^ Nagai Y, Ambinder AJ (Jul 8, 2023). "The Promise of Retinoids in the Treatment of Cancer: Neither Burnt Out Nor Fading Away". Cancers. 15 (14): 3535. doi:10.3390/cancers15143535. ISSN 2072-6694. PMC 10377082. PMID 37509198.
- ^ Esposito M, Amory JK, Kang Y (September 2024). "The pathogenic role of retinoid nuclear receptor signaling in cancer and metabolic syndromes". The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 221 (9): e20240519. doi:10.1084/jem.20240519. PMC 11318670. PMID 39133222.
- ^ Goodman GE, Thornquist MD, Balmes J, Cullen MR, Meyskens FL, Omenn GS, et al. (December 2004). "The Beta-Carotene and Retinol Efficacy Trial: incidence of lung cancer and cardiovascular disease mortality during 6-year follow-up after stopping beta-carotene and retinol supplements". Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 96 (23): 1743–1750. doi:10.1093/jnci/djh320. PMID 15572756.
- ^ Motamedi M, Chehade A, Sanghera R, Grewal P (2021-07-22). "A Clinician's Guide to Topical Retinoids". Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery. 26 (1). SAGE Publications: 71–78. doi:10.1177/12034754211035091. PMC 8750127. PMID 34292058.
- ^ Duester G (September 2008). "Retinoic acid synthesis and signaling during early organogenesis". Cell. 134 (6): 921–931. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.09.002. PMC 2632951. PMID 18805086.
- ^ Brzezinski P, Borowska K, Chiriac A, Smigielski J (July 2017). "Adverse effects of isotretinoin: A large, retrospective review". Dermatologic Therapy. 30 (4): e12483. doi:10.1111/dth.12483. PMID 28295859.
- ^ "Soriatane (Acitretin): Side Effects, Uses, Dosage, Interactions, Warnings". RxList. 2013-12-02. Archived from the original on 2013-12-02. Retrieved 2024-08-30.
- ^ a b Mukherjee S, Date A, Patravale V, Korting HC, Roeder A, Weindl G (2006). "Retinoids in the treatment of skin aging: an overview of clinical efficacy and safety". Clinical Interventions in Aging. 1 (4): 327–348. doi:10.2147/ciia.2006.1.4.327. PMC 2699641. PMID 18046911.
- ^ Duvic M, Nagpal S, Asano AT, Chandraratna RA (August 1997). "Molecular mechanisms of tazarotene action in psoriasis". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 37 (2): S18 – S24. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(97)80396-9. ISSN 0190-9622.
- ^ "Drug Approval Package: Aklief". US Food and Drug Administration. October 21, 2019. Archived from the original on 19 November 2019. Retrieved 31 December 2021.
- ^ Hall JA, Grainger JR, Spencer SP, Belkaid Y (July 2011). "The role of retinoic acid in tolerance and immunity". Immunity. 35 (1): 13–22. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2011.07.002. PMC 3418663. PMID 21777796.
- ^ Burri BJ, Clifford AJ (October 2004). "Carotenoid and retinoid metabolism: insights from isotope studies". Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics. Highlight issue on Carotenoids. 430 (1): 110–119. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2004.04.028. PMID 15325918.
- ^ Burri BJ, Clifford AJ (October 2004). "Carotenoid and retinoid metabolism: insights from isotope studies". Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics. Highlight issue on Carotenoids. 430 (1): 110–119. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2004.04.028. PMID 15325918.
- ^ Esposito M, Amory JK, Kang Y (September 2024). "The pathogenic role of retinoid nuclear receptor signaling in cancer and metabolic syndromes". The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 221 (9). doi:10.1084/jem.20240519. PMC 11318670. PMID 39133222.
- ^ "Systemic medications: Soriatane (acitretin)". National Psoriasis Foundation. Archived from the original on 13 June 2010. Retrieved 16 March 2018.
- ^ "Psoriasis - Diagnosis and treatment". Mayo Clinic. Archived from the original on 7 May 2017. Retrieved 16 March 2018.
- ^ Mukherjee S, Date A, Patravale V, Korting HC, Roeder A, Weindl G (2006). "Retinoids in the treatment of skin aging: an overview of clinical efficacy and safety". Clinical Interventions in Aging. 1 (4): 327–348. doi:10.2147/ciia.2006.1.4.327. PMC 2699641. PMID 18046911.
- ^ Kafi R, Kwak HS, Schumacher WE, Cho S, Hanft VN, Hamilton TA, et al. (May 2007). "Improvement of naturally aged skin with vitamin A (retinol)". Archives of Dermatology. 143 (5): 606–612. doi:10.1001/archderm.143.5.606. PMID 17515510.
- ^ Laosakul K, Chiewchanvit S, Chuamanochan M, Tovanabutra N (April 2022). "Acitretin treatment in antimalarial-refractory/intolerant discoid lupus erythematosus: A prospective, open-label, uncontrolled study". Lupus. 31 (5): 575–581. doi:10.1177/09612033221086878. PMID 35306922.
- ^ Panchal MR, Scarisbrick JJ (2015-02-03). "The utility of bexarotene in mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome". OncoTargets and Therapy. 8: 367–373. doi:10.2147/OTT.S61308. PMC 4322887. PMID 25678803.
- ^ Makimoto A, Fujisaki H, Matsumoto K, Takahashi Y, Cho Y, Morikawa Y, et al. (January 2024). "Retinoid Therapy for Neuroblastoma: Historical Overview, Regulatory Challenges, and Prospects". Cancers. 16 (3): 544. doi:10.3390/cancers16030544. PMC 10854948. PMID 38339295.
- ^ Makimoto A, Fujisaki H, Matsumoto K, Takahashi Y, Cho Y, Morikawa Y, et al. (January 2024). "Retinoid Therapy for Neuroblastoma: Historical Overview, Regulatory Challenges, and Prospects". Cancers. 16 (3): 544. doi:10.3390/cancers16030544. PMC 10854948. PMID 38339295.
- ^ Esposito M, Amory JK, Kang Y (September 2024). "The pathogenic role of retinoid nuclear receptor signaling in cancer and metabolic syndromes". The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 221 (9). doi:10.1084/jem.20240519. PMC 11318670. PMID 39133222.
- ^ Olson JM, Ameer MA, Goyal A (2024). "Vitamin A Toxicity". StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls. PMID 30422511. Retrieved 2024-08-15.
- ^ Esposito M, Amory JK, Kang Y (September 2024). "The pathogenic role of retinoid nuclear receptor signaling in cancer and metabolic syndromes". The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 221 (9). doi:10.1084/jem.20240519. PMC 11318670. PMID 39133222.
- ^ Goodman GE, Thornquist MD, Balmes J, Cullen MR, Meyskens FL, Omenn GS, et al. (December 2004). "The Beta-Carotene and Retinol Efficacy Trial: incidence of lung cancer and cardiovascular disease mortality during 6-year follow-up after stopping beta-carotene and retinol supplements". Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 96 (23): 1743–1750. doi:10.1093/jnci/djh320. PMID 15572756.
- ^ Alpha-Tocopherol BC (April 1994). "The effect of vitamin E and beta carotene on the incidence of lung cancer and other cancers in male smokers". The New England Journal of Medicine. 330 (15): 1029–1035. doi:10.1056/NEJM199404143301501. PMID 8127329.
- ^ Sherman SI (March 2003). "Etiology, diagnosis, and treatment recommendations for central hypothyroidism associated with bexarotene therapy for cutaneous T-cell lymphoma". Clinical Lymphoma. 3 (4): 249–252. doi:10.3816/CLM.2003.n.006. PMID 12672276.
- ^ "PRAC recommends updating measures for pregnancy prevention during retinoid use" (PDF). European Medicines Agency. Retrieved 2023-10-10.
- ^ "PRAC Seeks New Pregnancy Prevention Measures For Retinoids". Medscape. Retrieved 2023-10-10.
- ^ Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency. "Oral retinoid medicines: revised and simplified pregnancy prevention educational materials for healthcare professionals and women". GOV.UK. Retrieved 2023-10-10.
- ^ "Skincare Ingredients To Avoid During Pregnancy (+ List Of Harmful Chemicals In Beauty Products)". Little Baby Gear. 20 December 2022. Retrieved 2023-10-10.
- ^ "Is Vitamin A, Retinyl Palmitate and Retinol Safe for Pregnant Women?". Metrin Skincare. 26 May 2022. Retrieved 2023-10-10.
- ^ "Pregnancy-Safe Skin Care Guide: Ingredients to Avoid". What To Expect. Retrieved 2023-10-10.
External links
[edit]- Retinoids at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
